
本篇來介紹 Async Functions & await expression。
本文同步發表於 Titangene Blog:JavaScript 之旅 (6):Async Functions & await expression (1)
「JavaScript 之旅」系列文章發文於:
語法有以下幾種:
// Async function declaration
async function foo() {...}
// Async function expression
let foo = async function () {...}
// 或
let bar = async function foo() {...}
// Async method
let object = {
async foo() {...}
};
// Async arrow function
let foo = async () => {...}
Promise不管如何,Async function 的回傳值永遠是 Promise。
若 return 直接回傳值,回傳值會等同於將值傳入 Promise.resolve():
async function asyncFunc() {
return 'hi';
}
asyncFunc();
// Promise {<fulfilled>: "hi"}
asyncFunc()
.then(value => console.log(value));
// "hi"
若沒有回傳值,則等同於回傳 Promise.resolve(undefined):
async function asyncFunc() {
'hello';
}
asyncFunc();
// Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
asyncFunc()
.then(value => console.log(value));
// undefined
若 throw 某個值,回傳值會等同於將值傳入 Promise.reject():
async function asyncFunc() {
throw new Error('Oops');
}
asyncFunc();
// Promise {<rejected>: Error: Oops
// at asyncFunc (<anonymous>:2:9)
// at <anonymous>:5:1}
asyncFunc()
.catch(error => console.log(error));
// Error: Oops
// at asyncFunc (<anonymous>:2:9)
// at <anonymous>:1:1
Promise 的 then() vs. async / await在還沒有 async 和 await 之前,都是直接用 then() 和 catch() 來處理 Promise,如果一個 Promise 的結果值需要給其他 Promise 使用,就需在 then() 的 callback 內回傳另一個 Promise,而錯誤處理可在 then() 的第二個 callback,或是 catch() 處理。
例如:我要先從 /posts 這支 API 取得某篇文章是由哪個使用者發文的,然後在從 /users 這支 API 取得該使用者的 username:
const baseUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com';
function fetchJSON(url) {
return fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.catch(error => console.log(error));
}
function fetchPost(id) {
const apiURL = `${baseUrl}/posts/${id}`;
return fetchJSON(apiURL);
}
function fetchUser(id) {
const apiURL = `${baseUrl}/users/${id}`;
return fetchJSON(apiURL);
}
function main() {
const postId = 1;
fetchPost(postId)
.then(post => {
const userId = post.userId;
return fetchUser(userId);
})
.then(user => {
console.log(user.username);
});
}
main();
如果改用 async 和 await 會很像平常寫同步的寫法,不須將下一個步驟放在 then() 的 callback 中,且錯誤處理可在 try-catch 處理,不一定要在 then() 的第二個 callback 處理:
const baseUrl = 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com';
async function fetchJSON(url) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
return response.json();
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}
async function fetchPost(id) {
const apiURL = `${baseUrl}/posts/${id}`;
return fetchJSON(apiURL);
}
async function fetchUser(id) {
const apiURL = `${baseUrl}/users/${id}`;
return fetchJSON(apiURL);
}
async function main() {
const postId = 1;
const post = await fetchPost(postId);
const userId = post.userId;
const user = await fetchUser(userId);
console.log(user.username);
}
main();
明天會繼續介紹 Async Functions & await
先來看 InstantiateFunctionObject (實例化函數物件) 的定義:
OrdinaryFunctionCreate() 傳入的第一個參數 %AsyncFunction.prototype%,後面會提到傳入這個要幹嘛
深入看 OrdinaryFunctionCreate() 的定義:
OrdinaryObjectCreate() 的第一個參數 functionPrototype 就是剛剛傳入的 %AsyncFunction.prototype%,我們繼續往內鑽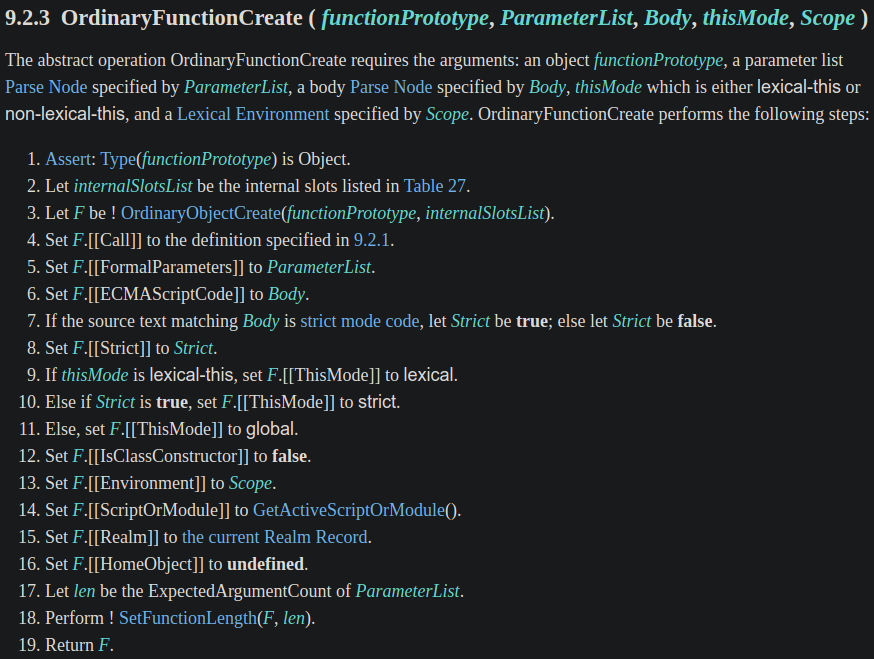
下面是 OrdinaryObjectCreate() 的定義:
O.[[Prototype]] 設為 proto」中的 proto 就是剛剛傳入的 %AsyncFunction.prototype%,所以到這邊的意思就是設定 prototype 為 AsyncFunction.prototype

在 AsyncFunction.prototype 的 spec 定義也有提到:
這就是為何我們建立的 async function 的 prototype 會是 AsyncFunction.prototype:
async function asyncFunc() {
return 'asyncFunc';
}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(asyncFunc));
// AsyncFunction {Symbol(Symbol.toStringTag): "AsyncFunction", constructor: ƒ}
且每個 async function 的 prototype 都是 AsyncFunction.prototype:
async function asyncFunc1() {
return 'asyncFunc 1';
}
async function asyncFunc2() {
return 'asyncFunc 2';
}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(asyncFunc1) === Object.getPrototypeOf(asyncFunc2));
// true
async function 與一般 function 的 prototype 不同:
async function asyncFunc() {
return 'asyncFunc';
}
function func() {
return 'func';
}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(asyncFunc));
// AsyncFunction {Symbol(Symbol.toStringTag): "AsyncFunction", constructor: ƒ}
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(func));
// ƒ () { [native code] }
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(func) === Function.prototype);
// true
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(asyncFunc) === Object.getPrototypeOf(func));
// false
但我們是無法透過寫 code 的方式碰到 AsyncFunction,因為 AsyncFunction 只是 spec 內部定義的東西。不過一般 function 的 prototype 就可以拿來使用:
console.log(Function.prototype);
// ƒ () { [native code] }
console.log(AsyncFunction);
// ReferenceError: AsyncFunction is not defined
接著來看 EvaluateBody 的定義:

下面是步驟 1 NewPromiseCapability() 的定義:用內建的 Promise constructor 來建立 Promise 物件,並提取其 resolve() 和 reject() 函數

步驟 2 FunctionDeclarationInstantiation() 的定義 (因太長就不截圖了) 大意上就是在建立 ECMAScript 函數的 execution context 時,會建立一個新的 function Environment Record,並在該 Environment Record 中實例化每個 formal parameter 的綁定,而 function body 中的每個宣告也都會被實例化,最後會回傳 NormalCompletion(empty)。
步驟 3 提到的 abrupt completion 指的是具有 [[Type]] 值,但不是 normal 的任何 completion。
[[Type]] 的值有包含這幾種:normal、break、continue、return 或 throw,[[Type]] 的值是用來代表發生 completion 的 type。
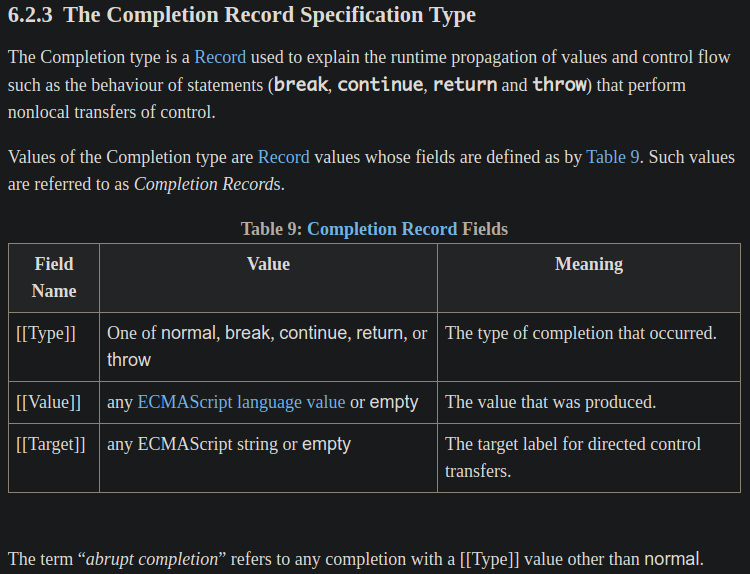
所以只要 declResult 不是 abrupt completion 就會執行 AsyncFunctionStart(),下面是 AsyncFunctionStart() 的定義:
result.[[Type]] 為 normal 時,等同於是執行 Promise.resolve(undefined)
result.[[Type]] 為 return 時,等同於是執行 Promise.resolve(result.[[Value]])
result.[[Type]] 一定為 throw),等同於是執行 Promise.reject(result.[[Value]])

明天會繼續介紹 Async Functions & await
